Understanding quality grades in mRNA synthesis: From research to GMP grade

This article highlights the importance of quality grades in mRNA synthesis from discovery phase to commercialization.
The field of mRNA synthesis has expanded rapidly, driven by advancements in therapeutics and vaccine development. Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the interest in mRNA-based vaccines has increased significantly, showcasing the potential of mRNA technology in addressing global health challenges including rare diseases. Whether you are conducting discovery phase studies or preparing for clinical trials and commercialization, selecting the right quality grade is essential for the success of your project.
mRNA Synthesis: a range of quality grades and their uses
Therapeutic mRNAs are preferably produced by in vitro transcription (IVT), a scalable method capable of achieving the quality required for clinical and commercial applications. mRNA can be synthesized in different grades: research-grade, GMP-like grade, and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP)-grade, each serving specific purposes and adhering to distinct standards (Fig.1).
Figure 1: mRNA drug development: From research and discovery to commercialization.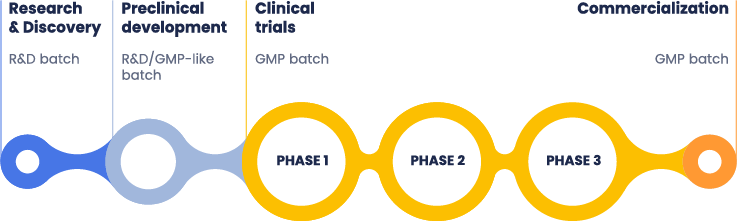
Research-grade mRNA: A standard quality for discovery stage
Research-grade mRNA meets basic standards for purity and consistency but does not comply with GMP regulations.
Key characteristics of research-grade mRNA include:
- Fast turnaround time for synthesis
- Cost-effective
- Basic quality control
Research-grade mRNA is the most suitable option for discovery stage in vitro studies, prioritizing rapid results and cost-efficiency. This grade supports initial data collection and feasibility analysis without the higher costs associated with GMP production.
During this phase, researchers can efficiently perform high-throughput screening, testing multiple mRNA sequences and processes to identify the most promising candidates for further development. By enabling quick iteration and screening, research-grade mRNA facilitates the selection of viable candidates for preclinical studies and potential progression to clinical trials.
GMP-like mRNA: An intermediary grade for pilot studies and process optimization
GMP-like mRNA serves as an intermediary grade between research-grade and full GMP. It offers enhanced mRNA quality control and production practices that use the principles of GMP standards, traceability in a non-controlled environment, and without full certification, while remaining cost-effective.
Key attributes of GMP-like mRNA include:
- Intermediate level of documentation and control
- Adherence to many GMP practices, though not fully certified
- Greater assurance of consistency compared to research-grade
GMP-like mRNA is a practical choice during the preclinical phase, particularly for:
- Pilot Studies: Generating material for testing in animal models to validate safety and efficacy before advancing to human trials.
- Process Optimization: Supporting the refinement of IVT protocols and scaling up production processes under conditions close to GMP standards.
While not permitted for human use, GMP-like mRNA provides researchers with a cost-efficient solution to advance their work with greater confidence. It ensures that the processes and quality controls established during this phase lay a solid foundation for subsequent clinical production, while maintaining the flexibility needed in early-stage development.
GMP-grade mRNA: The highest quality level for clinical trials and commercialization
GMP-grade mRNA represents the highest standard of mRNA production. This quality grade meets stringent regulatory requirements, ensuring the highest levels of purity.
Attributes of GMP-grade mRNA manufacturing include:
- Complete compliance with GMP guidelines
- Extensive quality assurance and testing protocols
- Detailed batch records and traceability for regulatory submission
- Suitable for clinical applications and eventual commercialization
The path to clinical trials and regulatory approval depends on careful planning and execution, including Investigational New Drug (IND) filing, Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (CMC) documentation, engineering batches , and Process Performance Qualification (PPQ).
Only GMP-grade mRNA fulfills the criteria for IND filing, which demonstrates to regulatory agencies like the FDA that the investigational product is of high quality. Central to this filing is the CMC section, which provides comprehensive details about the manufacturing process, quality controls, and product specifications. The CMC section gathers data from both engineering batches and PPQ.
Engineering batches are run before large-scale GMP production of the drug or vaccine to demonstrate the reliability of the process.
PPQ validates the reproducibility of the manufacturing process, ensuring it consistently produces mRNA batches that meet predefined quality standards for clinical and commercial use.
When advancing to clinical development, selecting GMP-grade mRNA ensures that the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) meets the most stringent quality standards to safeguard patient safety. It facilitates a smoother approval process, ensures reliability across clinical trials, supports large-scale production for commercialization, and certifies that the final mRNA-based drug or vaccine is suitable for use in humans, minimizing risks during clinical trials.
This meticulous approach not only accelerates your pathway to clinical trials but also sets the stage for commercial success.
Key differences between research-grade, GMP-like and GMP-grade mRNA
Selecting the right quality grade for your mRNA synthesis depends on your project’s phase and ultimate goals.
| Aspect | Research-grade mRNA | GMP-like mRNA | GMP-grade mRNA |
|
Purpose |
Non-clinical research and development |
Preclinical studies and process optimization |
Clinical vaccine and therapeutic trials |
|
Regulatory Standards |
No standards |
Follows many GMP practices but not fully certified |
Fully compliant with GMP regulations for manufacturing environment, processes, and specifications |
|
Quality Control |
Basic testing for purity |
Enhanced quality control, mimicking GMP |
Comprehensive testing for purity, integrity, and quantity |
|
Documentation |
Certificate of Analysis |
Intermediate documentation and control |
Extensive documentation for full batch traceability and CMC package |
|
Cost |
Lower production costs |
Moderate costs due to increased quality standards |
Higher costs due to stringent quality requirements |
|
Production Time |
Faster due to fewer regulatory requirements |
Moderate timeframes with added quality checks |
Longer due to rigorous testing and compliance |
|
Batch Consistency |
May vary across batches |
Improved consistency compared to research-grade |
High consistency across batches ensured through process validation |
|
Traceability |
Minimal traceability |
Partial traceability |
Full traceability, meeting regulatory needs |
|
Use Cases |
Early-stage research, feasibility analysis |
Pilot studies, preclinical validation, process optimization |
Clinical trials, IND submissions, commercial production |
Transitioning from research-grade to GMP-grade mRNA
As projects progress from the discovery phase to clinical development and commercialization, transitioning to GMP-grade mRNA is a critical step to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and support clinical applications.
Now that it’s clear there are different mRNA quality grades tailored to specific stages of development, one should consider earlier in the process, the future evolution of the mRNA early in the process. Recognizing that mRNA may advance to preclinical and clinical stages, careful planning from the outset can streamline this transition and avoid unnecessary delays.
A key aspect is selecting the right provider of raw materials and the appropriate quality grade for these materials. Ensuring that the raw materials meet the necessary standards for each stage of development minimizes risks of inconsistencies and regulatory challenges as the project evolves.
Equally important is partnering with a CDMO capable of supporting your project at every step—from research and preclinical optimization to GMP manufacturing. A CDMO with expertise across all stages should also have a robust Quality Management System (QMS) in place to ensure compliance, traceability, and consistency throughout the manufacturing process. This eliminates the need to qualify and validate multiple manufacturers and processes, reducing complexity while maintaining the highest quality standards.
By working with such a partner, you can save time, mitigate risks, and accelerate your timelines as your mRNA progresses toward clinical and commercial applications.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate quality grade for your mRNA synthesis is crucial to the success of your research, development, or clinical application. Understanding the distinctions between research-grade, GMP-like, and GMP mRNA allows you to align your production needs with your project’s objectives effectively.
By making the right choice, you can optimize cost, time, and regulatory compliance, ensuring your mRNA production supports a seamless progression from the discovery phase to commercial success.
Partnering with an experienced CDMO can make all the difference. With expertise and support across all quality grades, our team provides tailored solutions for each stage of your project, from research and preclinical optimization to GMP manufacturing. We are committed to guiding you through every step of the process, helping you mitigate risks, maintain consistency, and accelerate your development timelines.
Ready to advance your mRNA project?
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and learn how we can support your journey to clinical and commercial success.