MMP Assay kits
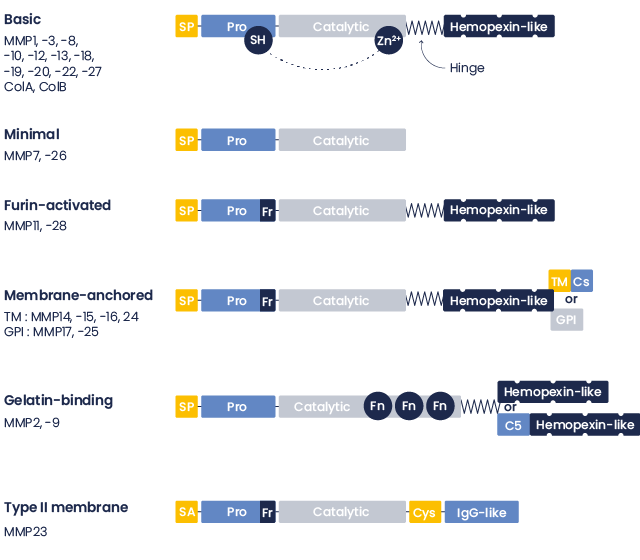
MMP Structure
This family currently includes more than 25 members that can be divided into collagenases (MMP-1, -8, and -13), gelatinases (MMP-2 and 9), stromelysins (MMP-3 and 10), matrilysins (MMP-7 and 26), and the membrane-type MMPs (MMP-14 to 17 and 24).
All MMPs have a similar domain structure:
- the pro-peptide,
- the catalytic domain,
- the hemopexin-like C-terminal domain (missing in some MMPs)
Figure : SP: signal peptide; Pro: pro-domain; Fr: Furin cleavage site; TM, transmembrane domain; Cs: Cytoplasmic domain; GPI: glycosyl-phospatidylinosital domain; Fn: fibronectin type motif; C5: type V collagen-like domain; SA: signal anchor; Cys: Cysteine array; IgG-like: immunoglobulin domain
A key role in tissue remodeling
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) belong to a family of secreted or membrane-associated zinc endopeptidases capable of digesting extracellular matrix components.
MMP-1
MMP-1 (collagenase-1) is involved in tumor development and metastasis and rheumatoid arthritis. It is proposed as a therapeutic target for these diseases.
MMP-2
MMP-2 (72-kDa gelatinase-A) is involved in tumor development and metastasis. It is proposed as a therapeutic target for cancer.
MMP-3
MMP-3 (stromelysin-1, transin-1) has been shown to involved in tumor metastasis3 and rheumatoid arthritis. Therefore, it is proposed as a therapeutic target for these diseases.
MMP-8
MMP-8 (neutrophil collagenase) is synthesized by neutrophils and stored in the specific granules until it is secreted. Human MMP-8 is a full-length pro-enzyme isolated from stimulated human neutrophil granulocytes.
MMP-10
MMP-10 (stromelysin 2) is involved in several pathological conditions, such as cancer, arthritis and wound healing.
MMP-14
MMP-14 (MT1-MMP), membrane-type MMP, plays an important role in tumor invasion. MMP-14 is expressed on the surface of invasive tumor cells, in stromal cells of human colon, breast, and head and neck carcinomas.